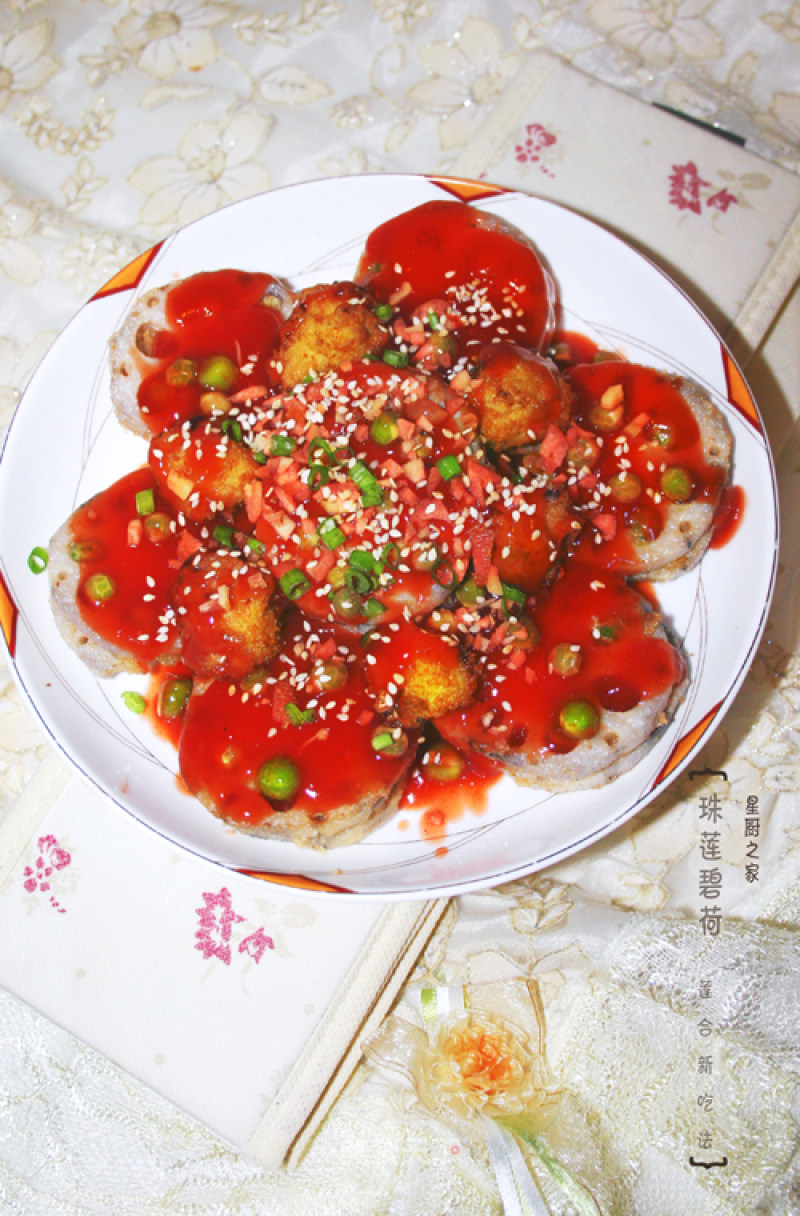
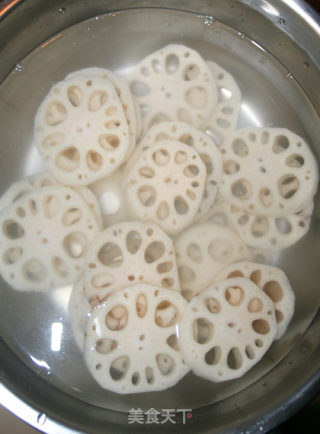
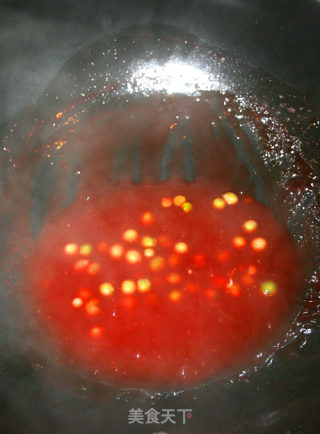
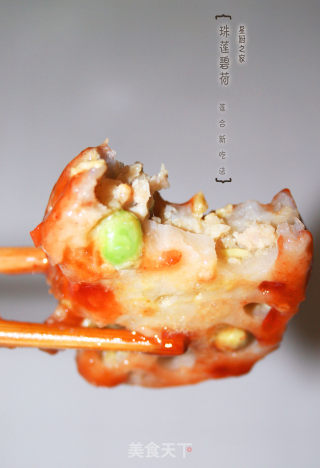
Zhulian Bihe
by Star Chef House
Favorite
Difficulty
Normal
Time
30m
Serving
2
Nutritional value of lotus root
1. Clearing heat and cooling blood: lotus root is used for cold nature, has the effect of clearing heat and cooling blood, and can be used to treat fever diseases; lotus root is sweet and rich in liquid, which is especially beneficial for fever, thirst, hemoptysis, hemoptysis and blood loss.
2. Laxative and antidiarrheal, invigorating the spleen and appetizing: lotus root contains mucus protein and dietary fiber, which can be combined with bile acid in the human body, cholesterol and triglycerides in food, and excrete it from the stool, thereby reducing lipids. absorb. The lotus root exudes a unique fragrance, and also contains tannins. It has the effect of invigorating the spleen and stopping diarrhea. It can increase appetite, promote digestion, appetite and invigorate, and is beneficial to those with poor appetite and loss of appetite to restore their health.
3. Replenishing blood and promoting muscle: lotus root has high nutritional value, rich in iron, calcium and other trace elements. It is also rich in plant protein, vitamins and starch. It can replenish qi and blood and enhance human immunity. Therefore, Chinese medicine calls it: "The main body nourishes the middle and nourishes the mind and strengthens the vitality."
4. To stop bleeding and dissipate blood stasis: lotus root contains a lot of tannins, which has the effect of constricting blood vessels and can be used to stop bleeding. Lotus root can also cool the blood and disperse blood. Chinese medicine believes that it can stop bleeding without leaving blood stasis. It is a good food therapy for febremia.
For people
suitable for majority of the people
1. It is especially suitable for old and young women and children, and those who are frail and sick. It is especially suitable for people with high fever, vomiting blood, hypertension, liver disease, loss of appetite, iron deficiency anemia, and malnutrition;
2. The lotus root is cold, so pregnant women should not eat it too early; the lotus root is cold, it is crisp and refreshing when eaten raw, but it hinders the spleen and stomach. People with poor digestive function of the spleen and stomach and loose stools should not eat it raw;
3. Oral administration of lotus root decoction is smooth and wide, and charcoal can stop bleeding and disperse blood stasis, and is used for various hemorrhagic diseases. Generally, eating lotus root after 1 to 2 weeks after childbirth can gradually relieve the problem.
Dosage
1. The lotus root can be eaten raw, cooked, mashed to drink, or dried and ground to cook porridge.
2. For edible lotus roots, choose the yellow-brown skin, thick and white flesh. If it is dark and has a peculiar smell, it is not suitable for consumption.
3. Raw lotus root cooked food is suitable for frying, stewing, frying and cooking ingredients, such as "eight treasures stuffed lotus root", "fried lotus root box" and so on.
4. Avoid using ironware when cooking lotus root, so as not to cause the food to turn black.
5. Uncut lotus root can be placed at room temperature for a week, but because the lotus root tends to turn black and the cut face is easy to rot, the cut lotus root should be covered with plastic wrap on the cut and kept fresh for about a week.
Efficacy and role:
Raw lotus root is sweet in taste, cold in nature, enters the heart, spleen, and stomach meridians;
It has the effects of clearing heat, promoting body fluid, cooling blood, dispelling blood stasis, invigorating the spleen, appetizing, and stopping diarrhea
Indications of fever, polydipsia, vomiting blood, blemishes, hot showers.
Ripe lotus root is warm in nature and sweet in taste;
It has the functions of invigorating the stomach and spleen, nourishing blood and replenishing, strengthening muscles, and antidiarrheal;
Indications of lung heat, cough, irritability and thirst, spleen deficiency, diarrhea, loss of appetite and various blood syndromes.
[Nature and flavor] sweet; cold [return meridian] heart; spleen; stomach; liver; lung meridian [functions and indications] clearing heat and promoting fluid; cooling blood; dispersing blood stasis; stopping bleeding. Mainly febrile polydipsia; vomiting; bleeding"
1. Clearing heat and cooling blood: lotus root is used for cold nature, has the effect of clearing heat and cooling blood, and can be used to treat fever diseases; lotus root is sweet and rich in liquid, which is especially beneficial for fever, thirst, hemoptysis, hemoptysis and blood loss.
2. Laxative and antidiarrheal, invigorating the spleen and appetizing: lotus root contains mucus protein and dietary fiber, which can be combined with bile acid in the human body, cholesterol and triglycerides in food, and excrete it from the stool, thereby reducing lipids. absorb. The lotus root exudes a unique fragrance, and also contains tannins. It has the effect of invigorating the spleen and stopping diarrhea. It can increase appetite, promote digestion, appetite and invigorate, and is beneficial to those with poor appetite and loss of appetite to restore their health.
3. Replenishing blood and promoting muscle: lotus root has high nutritional value, rich in iron, calcium and other trace elements. It is also rich in plant protein, vitamins and starch. It can replenish qi and blood and enhance human immunity. Therefore, Chinese medicine calls it: "The main body nourishes the middle and nourishes the mind and strengthens the vitality."
4. To stop bleeding and dissipate blood stasis: lotus root contains a lot of tannins, which has the effect of constricting blood vessels and can be used to stop bleeding. Lotus root can also cool the blood and disperse blood. Chinese medicine believes that it can stop bleeding without leaving blood stasis. It is a good food therapy for febremia.
For people
suitable for majority of the people
1. It is especially suitable for old and young women and children, and those who are frail and sick. It is especially suitable for people with high fever, vomiting blood, hypertension, liver disease, loss of appetite, iron deficiency anemia, and malnutrition;
2. The lotus root is cold, so pregnant women should not eat it too early; the lotus root is cold, it is crisp and refreshing when eaten raw, but it hinders the spleen and stomach. People with poor digestive function of the spleen and stomach and loose stools should not eat it raw;
3. Oral administration of lotus root decoction is smooth and wide, and charcoal can stop bleeding and disperse blood stasis, and is used for various hemorrhagic diseases. Generally, eating lotus root after 1 to 2 weeks after childbirth can gradually relieve the problem.
Dosage
1. The lotus root can be eaten raw, cooked, mashed to drink, or dried and ground to cook porridge.
2. For edible lotus roots, choose the yellow-brown skin, thick and white flesh. If it is dark and has a peculiar smell, it is not suitable for consumption.
3. Raw lotus root cooked food is suitable for frying, stewing, frying and cooking ingredients, such as "eight treasures stuffed lotus root", "fried lotus root box" and so on.
4. Avoid using ironware when cooking lotus root, so as not to cause the food to turn black.
5. Uncut lotus root can be placed at room temperature for a week, but because the lotus root tends to turn black and the cut face is easy to rot, the cut lotus root should be covered with plastic wrap on the cut and kept fresh for about a week.
Efficacy and role:
Raw lotus root is sweet in taste, cold in nature, enters the heart, spleen, and stomach meridians;
It has the effects of clearing heat, promoting body fluid, cooling blood, dispelling blood stasis, invigorating the spleen, appetizing, and stopping diarrhea
Indications of fever, polydipsia, vomiting blood, blemishes, hot showers.
Ripe lotus root is warm in nature and sweet in taste;
It has the functions of invigorating the stomach and spleen, nourishing blood and replenishing, strengthening muscles, and antidiarrheal;
Indications of lung heat, cough, irritability and thirst, spleen deficiency, diarrhea, loss of appetite and various blood syndromes.
[Nature and flavor] sweet; cold [return meridian] heart; spleen; stomach; liver; lung meridian [functions and indications] clearing heat and promoting fluid; cooling blood; dispersing blood stasis; stopping bleeding. Mainly febrile polydipsia; vomiting; bleeding"